Have you ever tried to use software that crashes every few minutes or requires endless updates? Imagine trying to manage your business like that—frustrating, right? That’s exactly why SaaS (Software as a Service) has become a game-changer for businesses and individuals worldwide.

With SaaS, you can access software online, anytime, without worrying about installations, upgrades, or complex setups. From cloud-based CRM systems to remote access software, SaaS allows you to work smarter, collaborate easily, and focus on growing your business instead of dealing with technical headaches.
In this article, you will discover everything about SaaS—its history, how it works, key benefits, architecture, challenges, pricing models, and the top SaaS products used by businesses today. By the end, you will understand what is a SaaS company, how cloud-based CRM software fits into the SaaS model, and how CRM in cloud computing can boost your business growth.
So, let’s dive in and explore the ultimate guide to SaaS in 2026!
Table of Contents
This guide is designed to help you explore every aspect of SaaS easily. You can jump to sections on SaaS architecture, compare SaaS vs traditional software, or get answers to frequently asked questions about software as a service.
We also provide real-life examples, case studies, and tables to simplify complex topics. Whether you’re a business owner looking for cloud-based CRM software or a student learning about remote desktop software, this guide covers everything you need.
What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
SaaS Simple Definition

SaaS is a cloud-based software delivery model. You access applications over the internet instead of installing them on your devices. Businesses no longer need to manage servers or hardware. This makes software easier, faster, and cheaper to use. Many organizations prefer cloud-based CRM systems or remote access software because it supports scalability and efficiency.
The model is based on subscriptions. Users pay monthly or yearly fees to access software. Updates and maintenance happen automatically. Platforms like Google Cloud Platform, Azure Cloud, and Firebase Hosting have accelerated SaaS adoption by providing reliable cloud hosting and cloud network security.
Imagine you run a small business and need a tool to manage customer contacts. Instead of buying software, installing it on your computer, and worrying about updates, you use Salesforce, a cloud-based CRM. You log in through your browser from anywhere, all updates happen automatically, and you pay a monthly subscription. This is exactly how SaaS works—software delivered over the internet, ready to use, with no installation hassles.
SaaS Real-World Explanation
Consider using TeamViewer remote access to help a client. You don’t install software locally on their PC permanently. Instead, you access it remotely using the cloud. Similarly, Gmail, Slack, and Salesforce are cloud-based CRM software you can access anywhere. SaaS allows this flexibility while keeping costs low.
Businesses love SaaS because it removes technical hurdles. Teams can collaborate, share data, and use apps from anywhere. Companies leveraging remote access programs or remote connection software see faster workflows and better productivity.
SaaS vs Traditional Software
| Feature | Traditional Software | SaaS Model |
| Installation | Local device | Cloud-based |
| Updates | Manual | Automatic |
| Cost | One-time license | Subscription (monthly/yearly) |
| Accessibility | Limited to device | Anywhere, any device |
| Maintenance | IT team required | Managed by provider |
Traditional software requires installation on each device, with upgrades and patches applied manually. On the other hand, SaaS applications are hosted in the cloud, offering remote software access, remote login software, and automatic updates.
Additionally, SaaS reduces upfront costs. You pay for usage rather than buying licenses, which is why businesses prefer what is SaaS business solutions over traditional software.
A Brief History of SaaS
1960 Mainframe → 1990 ASP → 2000 SaaS
Software delivery has evolved significantly. In the 1960s, mainframes dominated computing. By the 1990s, Application Service Providers (ASP) allowed limited remote software access. The 2000s saw modern SaaS solutions emerge, powered by cloud hosting and Google Cloud Services.
Today, cloud network security and private cloud hosting make SaaS secure and reliable. Businesses can scale, pay as they go, and access software globally using GCP, Google Cloud Hosting, or Azure Cloud.
Salesforce ka Role
Salesforce was a pioneer in SaaS. Its CRM platform demonstrated how cloud applications could replace on-premises software. Businesses could access data remotely and manage customer relationships without local installation.
This success inspired countless cloud-based CRM software solutions. Companies now integrate CRM in cloud computing for automation, analytics, and faster support.
Cloud Technology Evolution
Cloud computing has grown dramatically. Platforms like Google Cloud Platform Services, gcloud, and Google Cloud Next events showcase innovations in cloud storage services and remote access software. These services make SaaS scalable, secure, and flexible for enterprises.
How Does SaaS Work?
Have you ever wondered how you can log into a platform like Salesforce or Google Cloud Platform Services from any device without installing anything locally? That’s the magic of SaaS (Software as a Service). At its core, SaaS works by hosting applications on cloud storage services or Google Cloud Hosting. Instead of running software on your personal computer, everything happens on secure cloud servers. This allows businesses to use remote access software, remote login software, or even TeamViewer remote access to connect to their applications anytime, anywhere.
SaaS typically operates on a subscription model, where you pay monthly or annually for access. Updates, security patches, and feature enhancements happen automatically in the background, so you never have to worry about manual maintenance. Platforms like Azure Cloud, Firebase Hosting, and GoogleCloud provide the infrastructure for these applications, ensuring high performance and cloud network security. Many SaaS apps also use multi-tenant architecture, meaning a single instance serves multiple users while keeping each customer’s data private and secure.
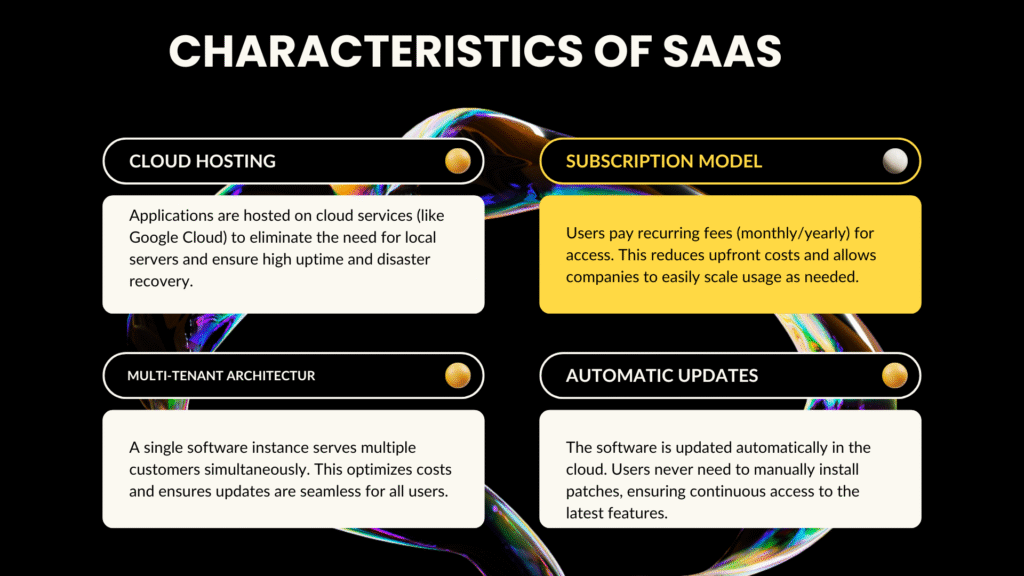
Cloud Hosting
SaaS applications are hosted on cloud storage services like GoogleCloud or Firebase Hosting. This eliminates the need for local servers. Users can log in from anywhere using remote desktop software or remote control software.
Cloud hosting ensures high uptime and disaster recovery. Businesses relying on Google Cloud Platform or Azure Cloud enjoy secure and reliable service for their daily operations.
Subscription Model
SaaS uses a subscription-based model. Users pay monthly, quarterly, or yearly fees depending on features. This approach reduces upfront costs compared to traditional software.
It also allows flexible access to remote access programs and TeamViewer remote access. Companies can scale usage without buying additional hardware.
Multi-Tenant Architecture
Most SaaS platforms use multi-tenant architecture, where a single software instance serves multiple customers. Each customer’s data is isolated. This approach optimizes costs and updates for everyone simultaneously.
Automatic Updates
SaaS apps update automatically in the cloud. Users do not have to install patches manually. Whether it is remote login software or cloud-based CRM, updates are seamless and continuous.
Key Characteristics of SaaS
Scalability
SaaS solutions are highly scalable. Businesses can increase users, storage, or features with minimal effort. Cloud network security and private cloud ensure that scaling does not compromise safety.
Pay-as-You-Go Pricing
SaaS often uses a pay-as-you-go model. Companies only pay for what they use, making software accessible for startups and large enterprises alike.
Accessibility from Anywhere
One of SaaS’s biggest advantages is global access. Users can log in from any device using remote desktop software, remote pc, or mobile apps.
Automatic Upgrades
Updates happen without downtime. New features, security patches, and enhancements are delivered automatically via cloud services like Google Cloud Platform Services.
High Availability & Uptime
Cloud-hosted SaaS platforms ensure high uptime. Remote access programs and remote software access are reliable, supporting businesses 24/7.
SaaS Architecture
Multi-Tenant Architecture
A single application instance serves multiple clients. Each client’s data remains private. This design saves cost and simplifies maintenance.
Single-Tenant Architecture
Some companies prefer dedicated servers. Private cloud solutions offer single-tenant architecture for enhanced control and security.
Data Security Layers
SaaS providers implement encryption, access control, and regular audits. Cloud network security and remote access software ensure sensitive data remains protected.
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
| Model | Definition | Example | Best Use Case |
| SaaS | Software delivered online | Salesforce, Gmail | End-user software access |
| PaaS | Platform for app development | Google App Engine | Developers building apps |
| IaaS | Infrastructure as service | GCP, Azure | Servers, storage, networks |
SaaS is ready-to-use software, PaaS is for developers, and IaaS provides raw infrastructure. Each has different pricing, control, and maintenance requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions About SaaS

What is a SaaS company?
A SaaS company is a business that provides software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Unlike traditional software that is installed on local computers, SaaS apps are hosted on the cloud, which allows users to access them from anywhere. Examples include Salesforce, Zoom, and Slack.
What is a SaaS app?
A SaaS app (Software as a Service application) is an online software tool that users access through a web browser or mobile app without the need for local installation. These apps handle all updates, security, and maintenance automatically. Popular SaaS apps include Dropbox, Canva, and Trello.
What are some SaaS examples?
SaaS examples include tools for business, education, and personal use:
- CRM & Sales: Salesforce, HubSpot
- Collaboration: Slack, Microsoft Teams
- Project Management: Asana, Trello
- Design & Creativity: Canva, Figma
- Storage & File Sharing: Dropbox, Google Workspace
What is SaaS in cloud computing?
SaaS is one of the three main cloud computing models (alongside PaaS and IaaS). In cloud computing, SaaS delivers fully functional software over the internet without any installation. Users pay on a subscription basis, and the provider manages hosting, security, and updates.
What is a SaaS website?
A SaaS website is the online portal where users can access a SaaS product. It usually includes product information, pricing plans, signup/login options, and customer support features. The website is also the main platform for marketing and lead generation for the SaaS company.
What is SaaS marketing?
SaaS marketing focuses on attracting, converting, and retaining users for software delivered via the cloud. It involves content marketing, email campaigns, free trials, onboarding guides, and customer retention strategies. The goal is to maximize subscriptions and minimize churn.
What is SaaS University?
SaaS University is an online educational platform that teaches how to build, market, and scale SaaS businesses. It offers tutorials, courses, and resources for developers, marketers, and entrepreneurs interested in the SaaS industry.
Conclusion
When I first started my small business, I remember struggling with software that constantly crashed and required endless installations. I spent hours trying to update tools, manage local servers, and figure out why my team couldn’t collaborate efficiently. Then, I discovered SaaS.
Switching to cloud-based CRM software and other SaaS model tools completely changed my workflow. I could access my data anywhere, help my team work remotely using remote desktop software, and make decisions faster with analytics and intelligence built right into the apps. Over time, I realized SaaS is not just software—it’s freedom. Freedom from technical headaches, freedom to scale, and freedom to focus on growing my business. Now, every time I log into Google Cloud Platform Services or check updates on Firebase Hosting, I feel how seamless and empowering what SaaS can truly be.
To dive deeper into SaaS and its features, you can check out my full guide here: Growzen SaaS Guide. I also found this Forbes article on cloud software helpful for understanding how businesses worldwide are leveraging SaaS solutions.
For anyone wondering whether to adopt cloud-based CRM, a cloud-based CRM system, or explore remote access programs, my advice is simple: start small, experiment, and let SaaS handle the heavy lifting. Once you experience it, you’ll understand why businesses worldwide are moving to the cloud. SaaS isn’t the future—it’s already here, and it’s transforming lives one app at a time.


Leave a Reply